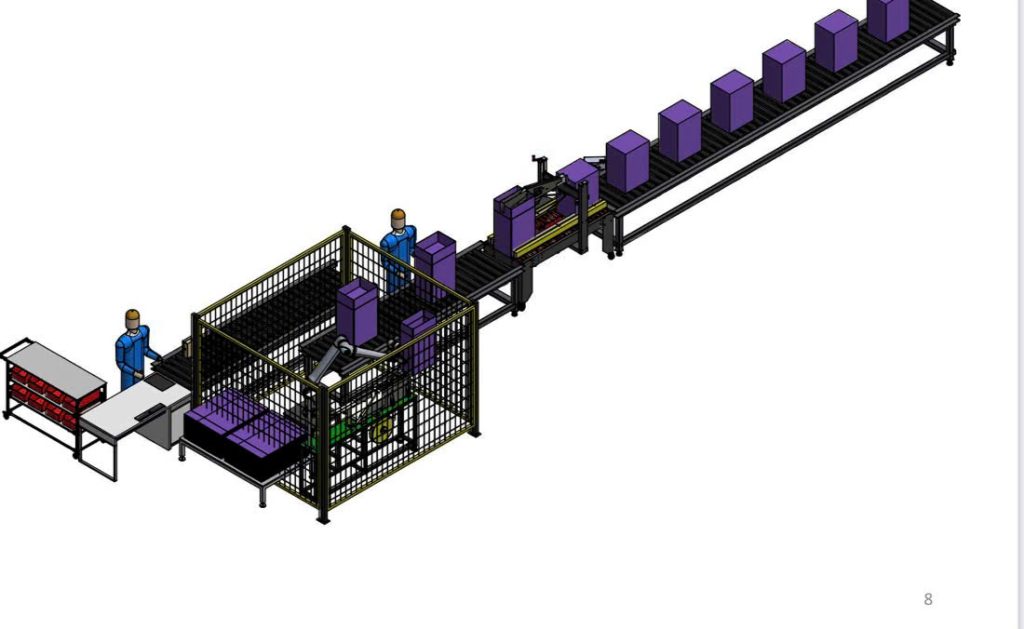
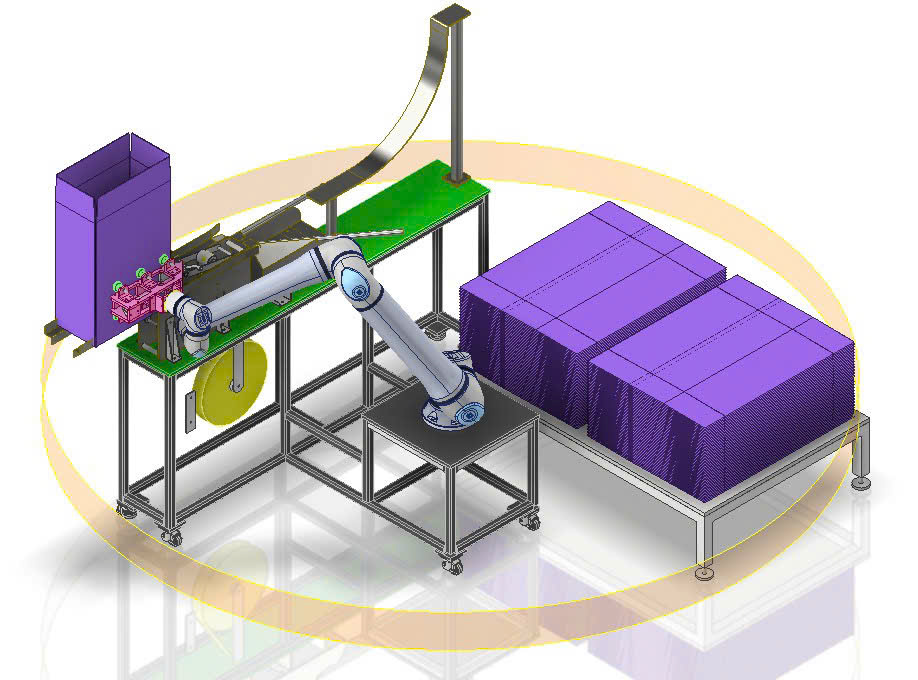
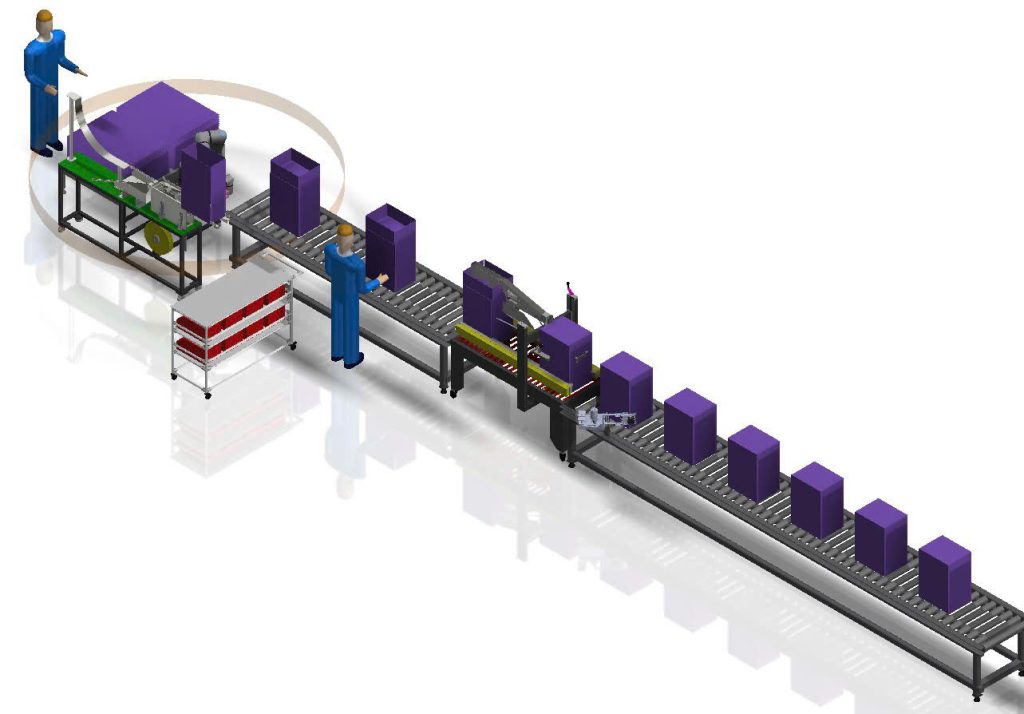
Automation is being researched and applied more and more widely in the field of industrial production, from robotic arms on production lines to Pick & Place technology participating in the operational machining process.
Tự động hóa là gì? Có rất nhiều khái niệm khác nhau về tự động hóa. Theo IBM, tự động hóa là việc sử dụng công nghệ để thực hiện các nhiệm vụ đầu vào, giúp giảm tải công việc của con người. Nó bao gồm các ứng dụng trong doanh nghiệp như: tự động hóa quy trình kinh doanh (BPA), tự động hóa công nghệ thông tin, tự động hóa mạng, tự động hóa tích hợp giữa các hệ thống; ứng dụng trong công nghiệp như robot,… Còn theo Từ điển Kinh tế học, Đại học Kinh tế Quốc dân: Tự động hóa (Automation) được hiểu là việc ứng dụng các giải pháp khoa học kỹ thuật hay các công nghệ tiên tiến vào quá trình sản xuất thông minh của ngành công nghiệp, nhằm giải phóng phần lớn hoặc hoàn toàn sức lao động của con người sang máy móc.
Dù được hiểu theo nghĩa nào thì bản chất chung của tự động hóa là ứng dụng công nghệ vào hoạt động sản xuất kinh doanh nhằm hạn chế tối đa lỗi hỏng từ lao động thủ công của con người, tối ưu hóa quy trình thủ tục, chi phí và mang lại hiệu quả cao.
Tại sao cần tự động hóa? Thông thường, tự động hóa được sử dụng để giảm thiểu lao động hoặc thay thế con người trong những công việc lặp đi lặp lại hoặc nặng nhọc nhất. Công nghệ tự động hóa hầu như có mặt ở tất cả các ngành dọc và ngóc ngách và nổi bật nhất là ứng dụng trong sản xuất, giao thông vận tải và an ninh. Ví dụ, hầu hết các nhà máy sản xuất sử dụng một số quy trình tự động dưới dạng dây chuyền lắp ráp robot. Con người được yêu cầu để xác định các quy trình và giám sát chúng, trong khi việc lắp ráp các thành phần khác nhau được giao cho máy móc. Máy móc sẽ tự động chuyển đổi nguyên liệu thô thành thành phẩm.
Trong lĩnh vực công nghệ, tác động của tự động hóa đang gia tăng nhanh chóng, cả trong phần mềm / phần cứng và lớp máy. Việc triển khai các công nghệ trí tuệ nhân tạo (AI) và học máy (Machine Learning) mới hiện đang thúc đẩy sự phát triển của lĩnh vực này một cách chóng mặt. Phân loại tự động hóa Phân loại tự động hóa theo quy trình BPA: Được hiểu là tự động hóa kinh doanh hoặc chuyển đổi số các quy trình kinh doanh phức tạp RPA: Tự động hóa quá trình robot chứa robot phần mềm (bot) bắt chước các nhiệm vụ của con người. IPA: Tự động hóa quy trình thông minh là một bộ công cụ quy trình kinh doanh có khả năng bắt chước các hoạt động của con người và theo thời gian sẽ ngày càng cải thiện các hoạt động đó. Phân loại tự động hóa theo hình thức sản xuất Tự động hóa cố định – Fixed automation: Đề cập đến một cơ sở sản xuất tự động trong đó trình tự của các hoạt động chế biến, sản xuất được cố định bởi cấu hình thiết bị-máy tự động cứng. Tự động hóa có thể lập trình – Programmable automation: Đây là một hình thức tự động hóa phổ biến để sản xuất sản phẩm theo lô. Theo đó, mỗi đơn đặt hàng mới, thiết bị sản xuất sẽ được lập trình lại và thay đổi để phù hợp với kiểu dáng sản phẩm mới. Tự động hóa linh hoạt – Flexible automation: Đây là cấp độ cao hơn của tự động hóa có thể lập trình được. Tại đây, không yêu cầu nhóm các sản phẩm giống hệt nhau thành lô; thay vào đó, một tập hợp các sản phẩm khác nhau có thể được tiến hành sản xuất.
Phân loại tự động hóa theo cấp độ Mức độ cơ bản: Ở cấp độ này, hệ thống automation sẽ đảm nhận các nhiệm vụ đơn giản, lặp đi lặp lại và thực hiện lại các tác vụ này hoàn toàn tự động. Mức độ quy trình: Tự động hóa ở cấp độ này cho phép máy móc có thể thực hiện các quy trình nhiều bước với mức độ phức tạp cao và lặp lại chúng bằng cách tích hợp với nhiều hệ thống. Mức độ tự động hóa thông minh: Là cấp độ tự động hóa cao nhất. Ở cấp này, công nghệ tự động hóa có thể tích hợp với trí tuệ nhân tạo (AI) và mô hình học máy (Machine Learning) để liên tục học hỏi và đưa ra hành động tốt hơn dựa trên dữ liệu từ các tình huống trong quá khứ đã xảy ra và phân tích chúng.
Controllers used in automation PID controller PID (Proportional Integral Derivative) is a control loop feedback mechanism widely used in industrial control systems. The PID controller calculates the error value as the difference between the measured value of the variable parameter and the desired set value. The PID will perform the maximum error reduction by adjusting the input control value. To achieve the best results, the PID parameters used in the calculation must be adjusted according to the nature of the system - while the control type is the same, the parameters must depend on the characteristics of the system. PID is considered to be the ideal controller of modern process control systems. It is used in most of the current industrial automatic process control applications in regulating flow, temperature, pressure, etc. Sequential controller and logical sequential control Sequential controller and logical sequential control are specialized computers used to control machinery and production processes. Users, through programming languages, can build their own algorithms to solve any production machinery control problems. Not only that, during use, the algorithm can be flexibly adjusted to suit changes in production conditions. Computer controller This is a controller performed by a computer with two main functions: continuous control and feedback control throughout the factory. Accordingly, a single computer can perform the operations of hundreds of controllers, including data from a network of PLCs, instruments and controllers to perform typical (such as PID) control of many individual variables or in some cases, to perform complex control algorithms using multiple inputs and mathematical operations. Outstanding benefits of automation in production Applying automation technology will bring businesses outstanding benefits, solving economic problems that any business management board faces, while bringing increasingly better product quality. Below are the important benefits of applying automation in industrial production:
Reducing labor costs This is the first benefit that businesses aim for when wanting to apply automation. Instead of reducing investment costs for machinery, cutting labor seems to be a more optimal solution because it does not reduce product quality. Factory automation will solve the labor of workers, from which businesses can reduce labor, save costs to increase profits. Reduce operating costs Automatic robots can complete tasks with the productivity of 3-5 people, depending on different jobs. In addition to saving labor costs, using automatic machines helps to arrange the process reasonably, increase the accuracy in the operation of each stage, and minimize the risk of wasting raw materials during operation. Safe working environment With the characteristics of the manufacturing industry, which often has to be exposed to and work in a relatively dangerous environment, the application of automation technology helps improve the working environment, helping people not to have to perform jobs beyond their capacity and come into contact with unsafe machines. Reduce production time Automation will help save a significant amount of time compared to traditional manual processing or outsourcing. Improve labor productivity Unlike humans, who can only work for a certain period of time and then have to rest, robots or technologies in the automation process are capable of working 24/7 at a constant speed, without supervision and can still operate with absolute precision. From there, work efficiency will be maintained, work productivity will be significantly improved.
Impact of automation on workers The 4th industrial revolution has created many breakthroughs in new technologies in areas such as artificial intelligence production, manufacturing, industrial robot arms, internet development, AGV self-driving vehicles, 3D printing technology, nanotechnology, biotechnology, materials science, energy storage and informatics. Along with that, automation combined with artificial intelligence (AI) will develop more strongly, even with skills that were previously only possessed by humans, machines can now replace part or all of them.
The development of automation technology will help free up human labor, increase labor productivity but also put millions of people at risk of losing their jobs. Accordingly, the application of automation technology will lead to serious job losses for workers. Jobs at risk of being eliminated or drastically cut include: Repetitive work; transactions that do not require employees to have a degree, only based on standard procedures such as financial transactions... However, each business and each worker must also have a correct understanding of the relationship between people and technology.